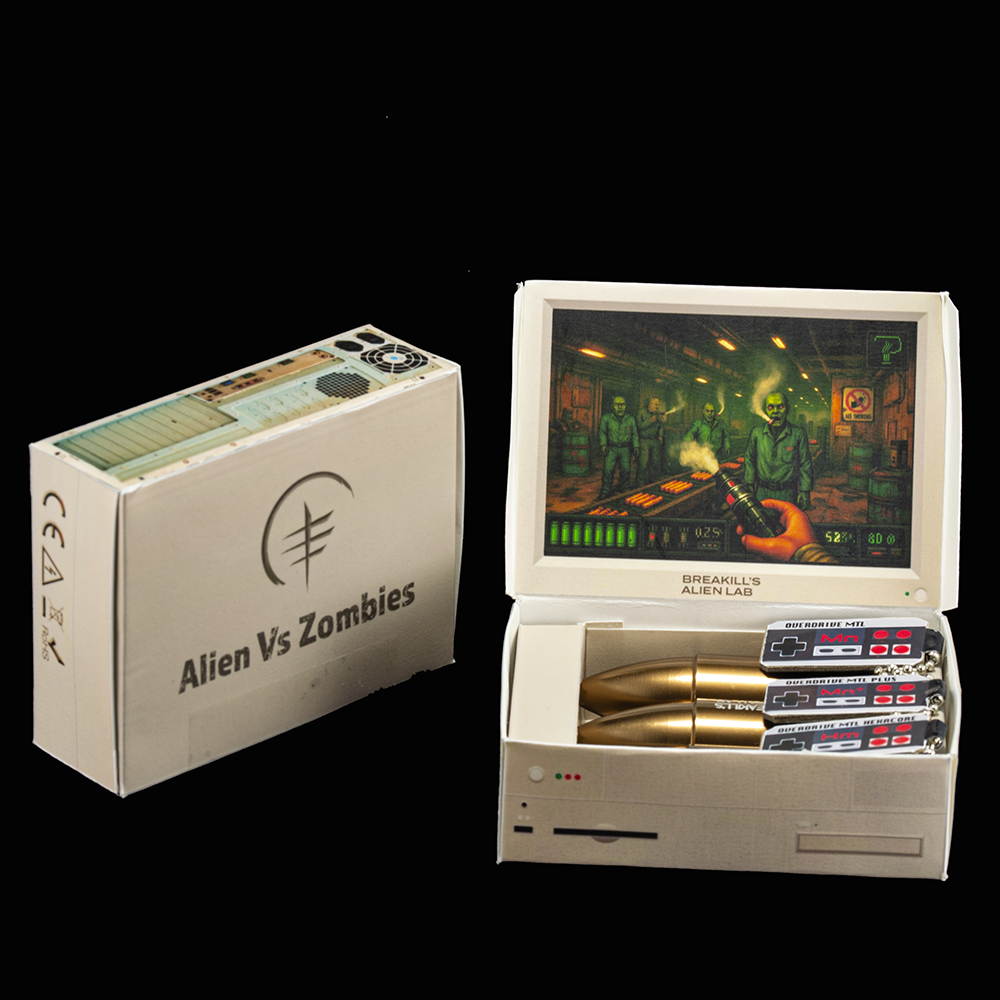
Make this Halloween one to remember with a truly special drop. The star is the MTL Hexacore Alien, our most refined MTL coil to date, delivering standout brightness and silky roundness. The retro-gaming collector’s box with bullet packaging also grants access to Multicore Nano Plus—an enhanced variant of the beloved Multicore MTL, tuned for higher wattages on regulated or mech setups for extra hit and flavor.
Note: all coils are wrapped clockwise.
Senza categoria
Have no fear! We got you covered!
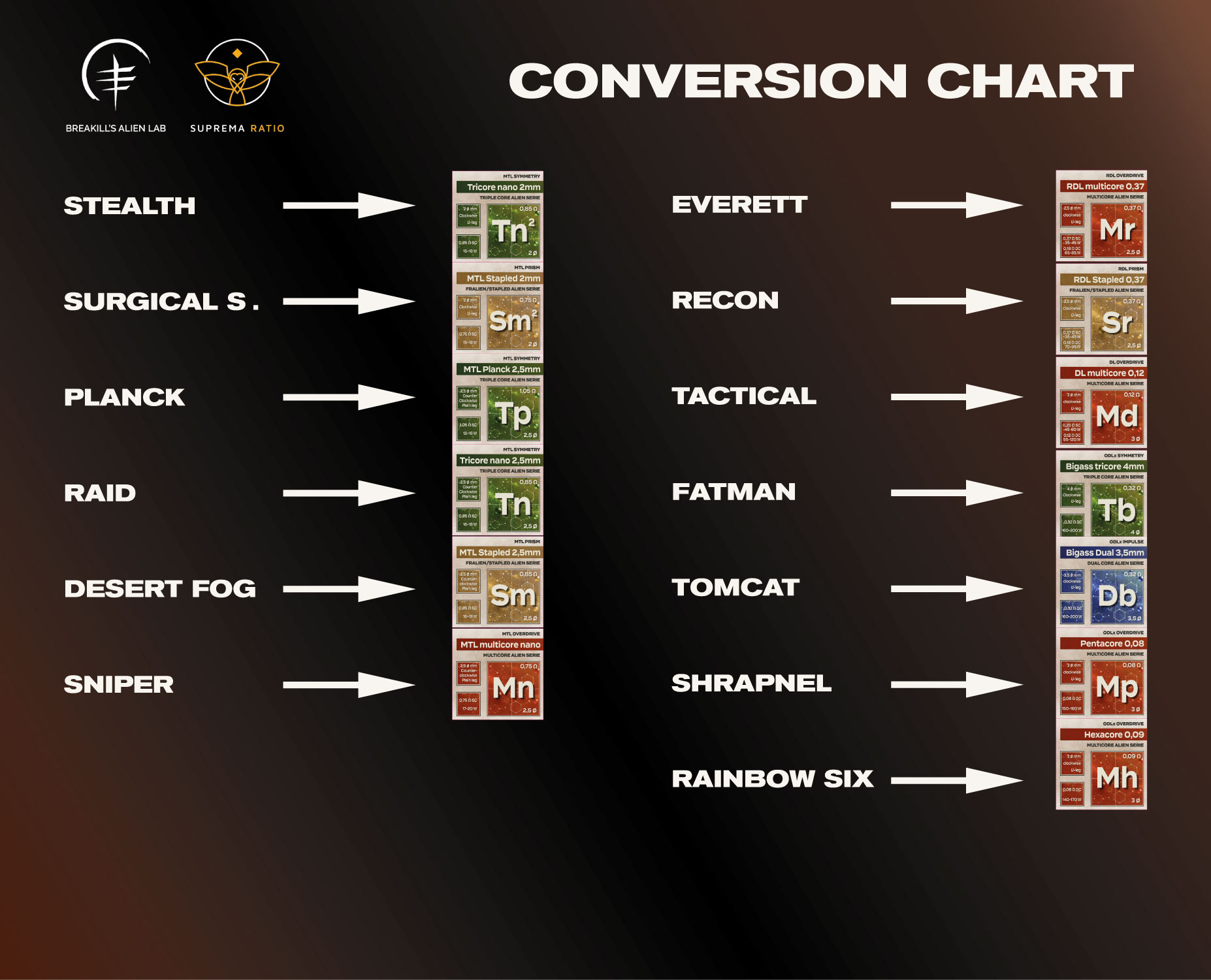
Many models has been kept and converted into the new “the lab” collection!
The conversion chart will help you finding them, and find the great classics into the giant new collection!
We promised big surprises—here they are!
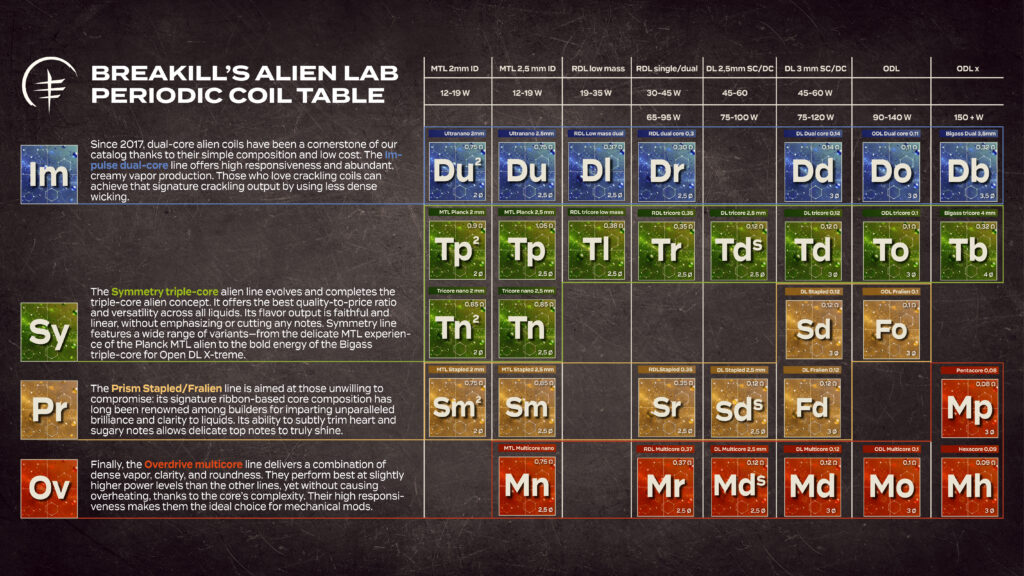
A collection of 31 coil models, both new and classic, combined into our most comprehensive selection ever! The new 2025 catalog revolutionizes the LAB’s offerings in every vaping style, power range, and flavor output.
Plus, all Suprema Ratio wires and spools are now 20% off forever!
DOWNLOAD THE NEW CATALOG HERE:
https://shop.breakill.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/CAT_ENG_25_LQ_compressed.pdf
In the world of vaping, the choice of coil material is crucial for determining performance, durability, and safety. Among the most commonly used materials are Kanthal and Nichrome, each with its own unique history and specific properties.
History and Composition
Nichrome is an alloy primarily composed of nickel and chromium, developed in the early 20th century. Thanks to its high resistivity and oxidation resistance, it quickly became a popular choice for heating elements in industrial furnaces and household appliances.
In the 1930s, engineer Hans von Kantzow introduced Kanthal, an alloy based on iron, chromium, and aluminum. This new composition offered longer durability and a higher maximum operating temperature compared to Nichrome.
Differences Between Kanthal and Nichrome
- Resistivity and Reactivity:
Nichrome has lower resistivity than Kanthal, making it more reactive and enabling faster heating. This translates to smoother output and a flavor profile often preferred by many vapers. - Maximum Operating Temperature:
Kanthal can operate at higher temperatures, up to 1425°C, compared to Nichrome’s limit of 1250°C. This makes it ideal for applications requiring extreme heat. - Durability and Stability:
Kanthal offers up to four times the lifespan of Nichrome, due to the formation of a protective aluminum oxide layer that prevents oxidation and corrosion.
Resistance to Temperature and Corrosion
Kanthal, with its aluminum content, forms an aluminum oxide layer that provides effective protection against oxidation at high temperatures. However, in humid environments or when exposed to aggressive chemicals, this layer may be less resilient.
Nichrome, on the other hand, forms a chromium oxide layer. Although this layer is less heat-resistant compared to aluminum oxide, it provides good protection in chemically aggressive environments. This makes Nichrome more suitable in scenarios where resistance to corrosion is a priority.
Passivation and Preheating
There is a widespread belief that preheating Nichrome coils is harmful. In reality, controlled preheating promotes the formation of the chromium oxide layer, a process known as passivation, which improves the material’s resistance to corrosion caused by e-liquids.
For Kanthal, passivation occurs naturally during use, forming an aluminum oxide layer. However, this layer can be less resistant in chemically aggressive environments, making Kanthal more susceptible to corrosion in such conditions.
Conclusion
The choice between Kanthal and Nichrome depends on the specific needs of the vaper. Kanthal offers greater durability and resistance to high temperatures, while Nichrome ensures superior reactivity and better corrosion resistance in chemically aggressive environments. Understanding the properties of each material and their associated passivation processes is essential to optimize the vaping experience and ensure user safety.
sources:
https://www.kanthal.com/it/knowledge-hub/inspiring-stories/unalternativa-migliore-al-nichel